Strategic Effectiveness Team Report 2020
Intentional Focus #3 Strategic Effectiveness Team Report
Date of Meeting: September 21, 2020
Members in attendance: Chris Kearns, David Eitle (for David Cherry), Tracy Dougher, Ian Godwin, Megan Lasso, Tami Eitle (unable to attend Stephanie Gray, Chris Livingston).
Institutional Performance Indicators identified for IF 1 effectiveness and for mission fulfillment determinations:
|
Intentional Focus 1: Performance Indicators (Current Trends) (see Appendix 1 for current data and trends)
|
Threshold, by 2024 |
|
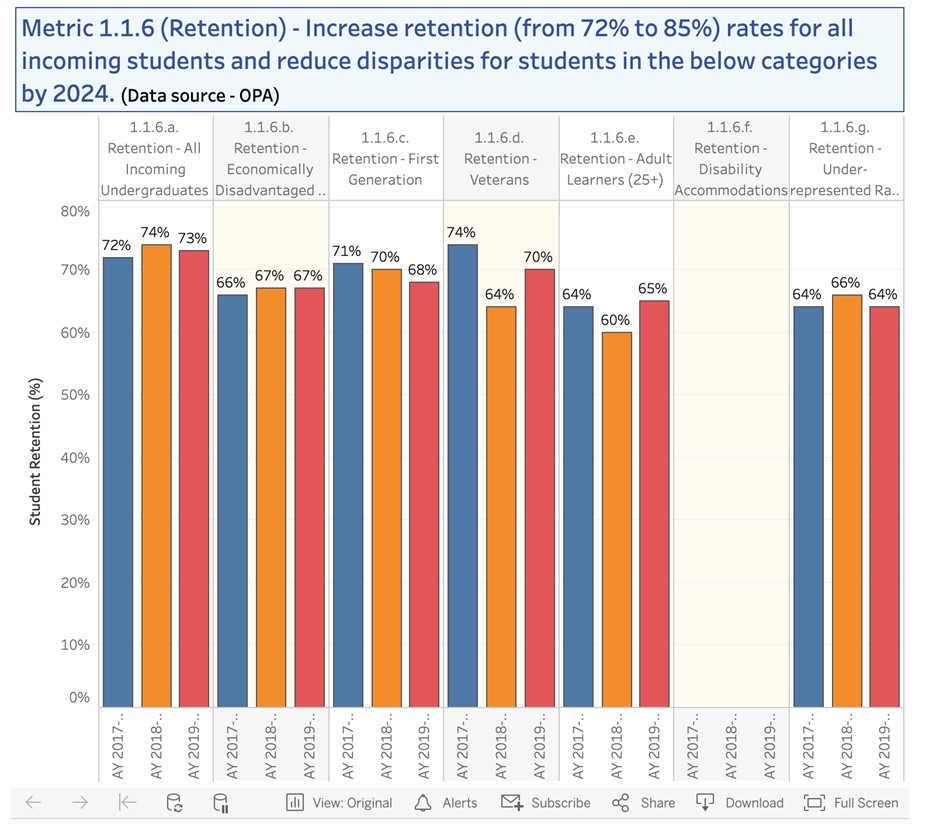
Metric 1.1.6 First-year retention rates (by group)* |
Metric 1.1.6. >77% overall; improve for all subgroups |
|
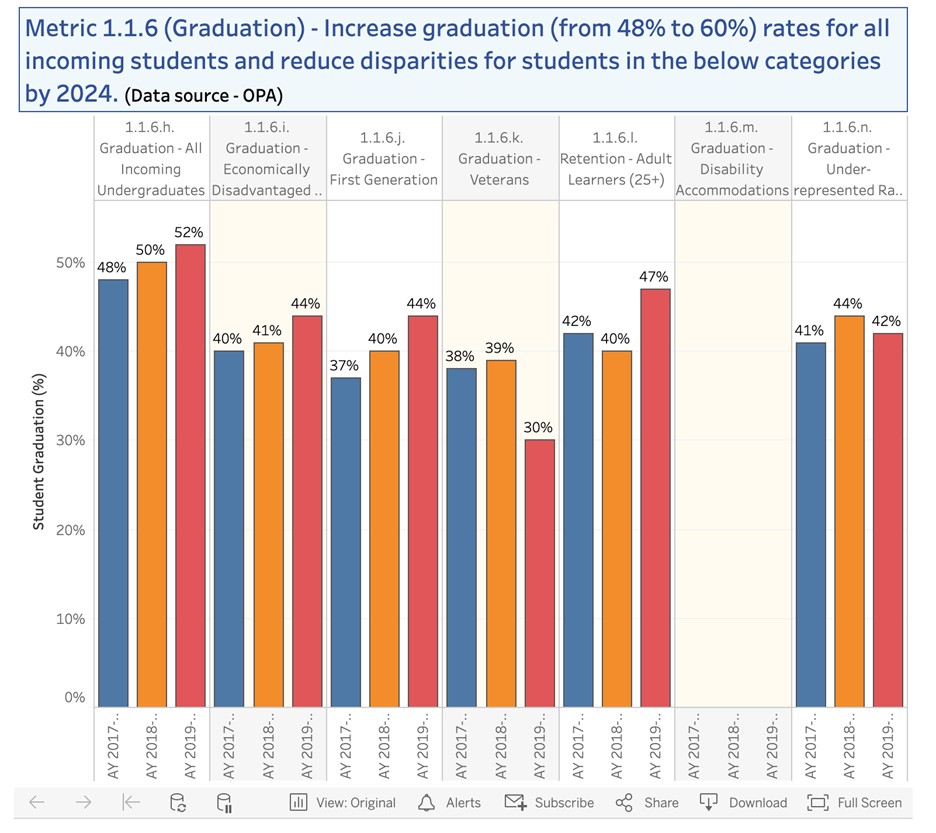
Metric 1.1.6 Six-year graduation rates (by group)* |
Metric 1.1.6 >56%; improve for all subgroups |
|
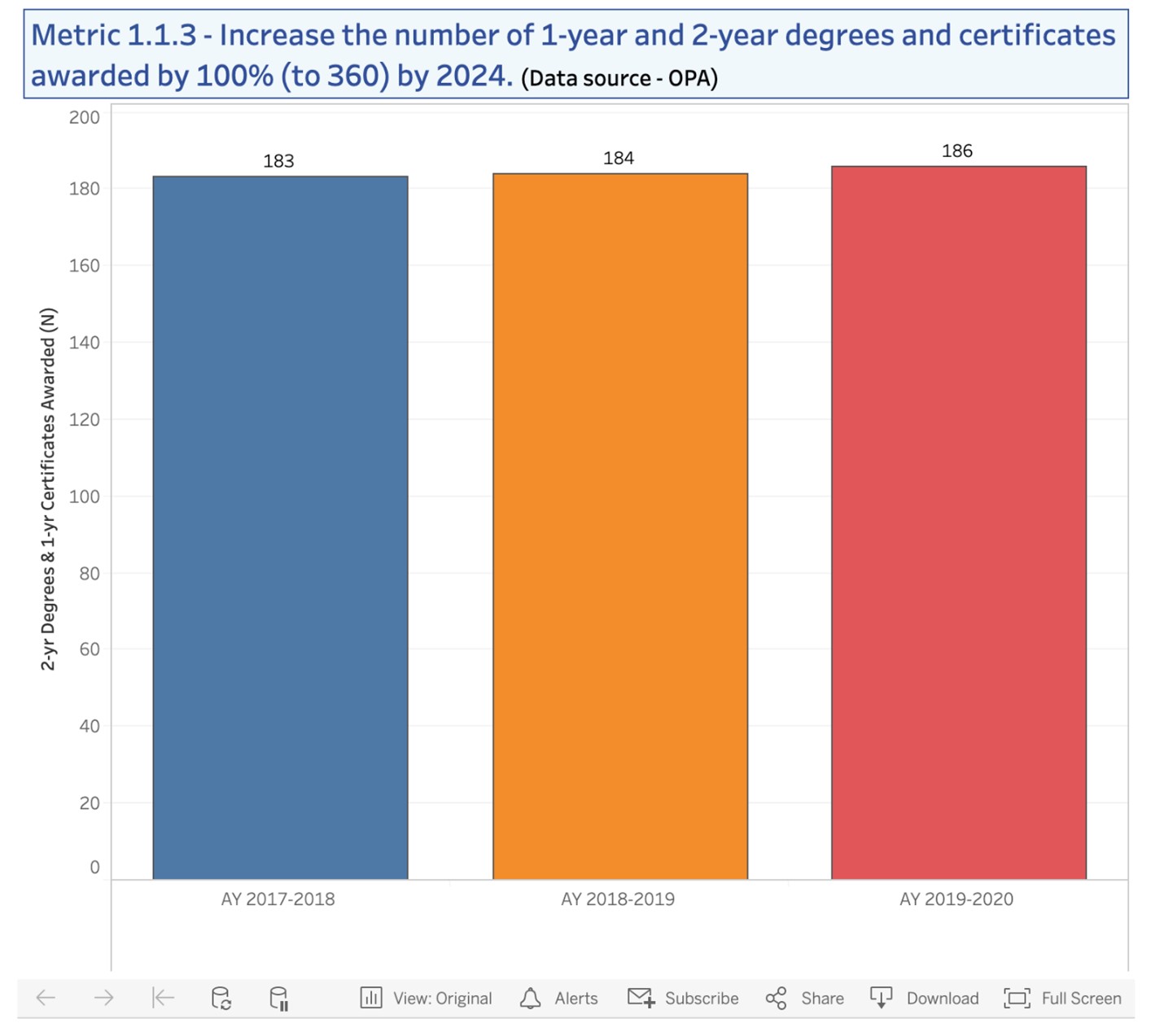
Metric 1.1.3 Gallatin College degrees and certificates awarded |
Metric 1.1.3 >200 |
|
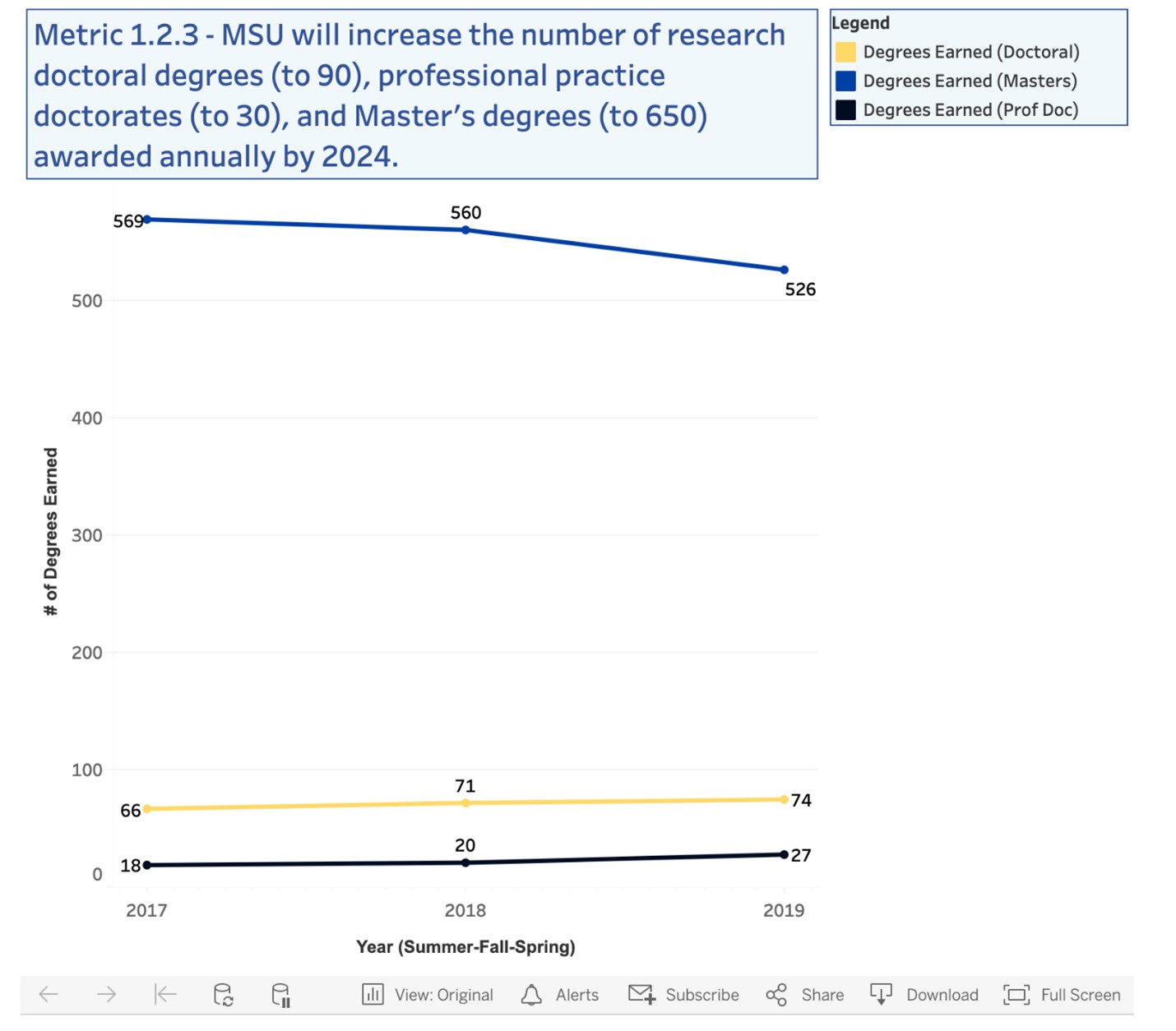
Metric 1.2.3 Graduate degrees awarded (Doctoral, Professional Practice Doctoral, Masters Degrees) |
Metric 1.2.3 >600 Masters and >90 Doctoral and >30 Professional Practice Doctorates |
|
Metric 1.3.2 Student proficiency in MSU Core Qualities |
Metric 1.3.2 MSU will improve proficiency rates for MSU Core Qualities |
Challenges that IFSET identified in the assessment exercise:
- Templates were clearly confusing for the units and so we need to work to improve the match between what we are assessing and what the units are reporting on. This may require revising the templates and assessment tool.
- Some of the assessment reports provided interpretation without summarizing the underlying data. The IFSET was left to just trust the interpretation of the unit and in most cases members of IFSET were familiar enough with the efforts of our peers on campus that we could fill in some blanks. However, a new template should make it clear that the report should include the actual performance metrics and thresholds for those metrics.
- Units should report out on specific strategies and not everything they do. For example, the group appreciates that AYCSS does lots of assessment and uses data mining to direct resources to the students who need those resources the most. However, a report on all their programs together does not provide the kind of detailed data and assessment of individual programs that allows for an understanding of which efforts are linked to various types of success. Some programs we already know have great impact and purposeful and thoughtful scaling up of those programs could be beneficial ways to reduce achievement gaps.
Suggestions for units to improve assessment:
- There is a need for units to clarify how the outcomes they are tracking align with the IF #1 performance indicators and importantly how they related to reducing group differences in some of the Strategic Plan (SP) indicators like retention and graduation rates.
- Help units to not just link their strategies to the SP goals like we ask them to do when they seek initial or additional investments in their strategies, but to actually think about how they would define success for the strategy and how that will drive the SP performance indicators in the right direction. For example, some strategies may focus on specific populations of students in order to provide them with the skills they need to be successful leading to the reduction of learning gaps between groups of students (Hilleman Scholars Program) and other strategies may touch every student and help increase retention and graduation for all (Core).
Graduate School (Total score=6.125)
Strategies: Efforts to increase degree completion rates for all demographic groups, increase enrollment in current and new professional grad programs.
Performance: The Graduate School is moving towards the metrics that it has identified, but IFSET questioned whether these are appropriate metrics (1.625)
Appropriateness: The strategies the Graduate School is using are well aligned with the SP indicators, but the performance indicators that the Graduate School is using to measure their performance are not well aligned with their own strategies. They should think more carefully about what metrics they are tracking and how these help them assess success of their strategy and how they align with the institutional indicators. (1.875)
Assessment: The Graduate School presented several indicators to measure success of their strategies including first year retention and tuition revenue from professional programs. However, these metrics did not seem to align with the strategies they were trying to assess and the strategies were really framed as goals (increasing degree completion rates across all demographic groups and Increasing enrollment in professional graduate programs). We actually think that the strategy the Graduate School should be assessing their efforts to increase the number of professional graduate degrees and certificates. They could track metrics like the number of professional programs and the number of graduates from these programs which would be related to the larger SP metric of Graduate Degrees Awarded (1.125)
Environmental Responsiveness: The Graduate School acknowledged that they have had to pivot towards a heightened focus on the student well-being and basic needs during the COVID-19 crisis and the Dean is focused on working with academic colleges and departments to develop stackable certificates that can help working adults advance their careers. (1.5)
MSU Core Assessment (Total score=7.75)
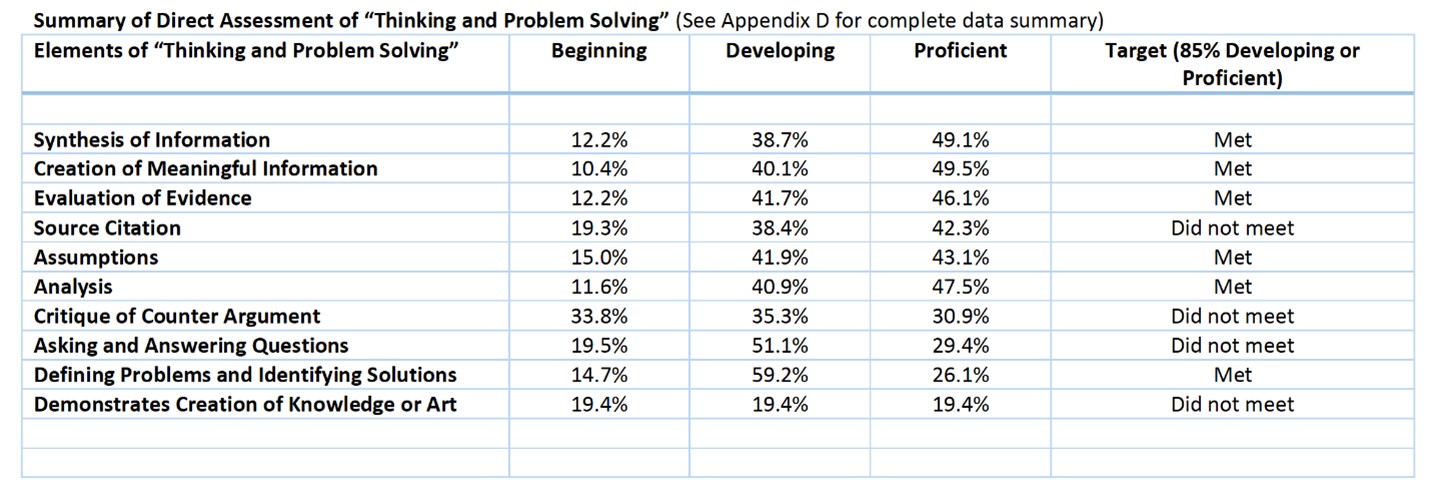
Strategies: Offer more Core teaching and assessment trainings and activities (Faculty Learning Communities), implementation of new MSU Core Qualities, assessment of “Thinking and Problem Solving” and design and improvement of Core program assessment.
Performance: The initial assessment of the first MSU Core Quality “Thinking and Problem Solving” occurred before the new Core Qualities were officially approved and served as a baseline for student performance. Participation by faculty in training for both teaching and assessing Thinking and Problem Solving in their courses was good for the initial assessment. (2)
Appropriateness: The assessment strategy aligns with the IF goals to offer high-quality, high impact teaching and learning for every student. (2.625)
Assessment: Initial assessment of “Thinking and Problem Solving” is being used to improve training for faculty in the teaching and assessment of this Core Quality in order to improve student outcomes. Assessment also sought input from stakeholders on how to improve future assessment practices. (1.375)
Environmental Responsiveness: The Core Committee demonstrated responsiveness by listening to those who participated in assessment and will revise assessment to differentiate between upper and lower division classes as well as try to reduce the burden on those faculty participating in assessment by randomly selecting from classes submitting student artifacts. (1.75)
AYCSS (Total score=6.75)
Strategies: Hilleman Scholars, Second Wind, Adventures MSU, Return to Learn, 1893 Scholars, Champchange
Performance: While thresholds for performance were not identified, performance data was presented for most programs. IFSET knows that AYCSS is using data to track performance and to inform programming. (2.25)
Appropriateness: Strategies seem to be well aligned, but individual metrics for some of the programs are more difficult to see as aligned to the SP indicators. However, AYCSS reported on a lot of programs within this one report and so provided minimal details on each. (1.875)
Assessment: AYCSS holds weekly metric meetings to help track success and to appropriately target students for programming or develop or alter programming to meet student needs. While it was not obvious from this assessment that they are using data to inform programming, that certainly does not mean that they are not doing so. (1.375)
Environmental Responsiveness: While it was not addressed directly, the fact that AYCSS tracks the characteristics of MSU students, tracks outcomes for students, and uses data to identify students with the greatest need for additional resources is an example of environmental responsiveness that the IFSET team knows is happening. (1.25)
Sophomore Surge (Total score=5.375)
Strategy: Sophomore Surge which include pairing peer mentors with first-year students in sections of the University Seminar
Performance: This is a relatively new program which is only beginning to develop assessment practices. Aside from first-year retention, many of the metrics are still fuzzy and are not being tracked. Currently the performance being tracked is the retention rate for those participating in University Seminar classes with a surge mentor and so that can be compared to overall retention. Multiple years of data are not yet available and while the program shows promise on some fuzzy metrics, better data will be needed in order to learn whether the program increases first-year retention. (1.5)
Appropriateness: There is a clear alignment with retention for the surge students, but the program does not seem to be formally tracking the impact for surge mentors who might also benefit from participation. (2.25)
Assessment: The team generally agreed that assessment has been minimal and advised that the Sophomore Surge develop and assessment plan in consultation with its leadership, the Assistant Provost, and the Office of Planning and Analysis. (0.875)
Environmental Responsiveness: There was no real response to this issue, certainly the program was initially responsive to the need to increase retention of students. (0.75)
Gallatin College (Total score=7.75)
Strategies employed: Co-requisite developmental courses, Analysis of areas where degree completion is lagging, .5 FTE staff to increase transfer to MSU
Performance: GC is tracking data on developmental and co-requisite completion rates and are already nearing the threshold set for 2024. Regular meetings to discuss degree and certificate completion as well as recruitment and retention in programs are held to identify program areas where improvements are needed. OPA has worked with GC and they will be able to track GC transfer to MSU in future reports. (1.875)
Appropriateness: Metrics tracked are well aligned with the SP performance indicators (2.625)
Assessment: The assessment process includes appropriate individuals and groups and is widely shared to inform decisions about improving or expanding existing programs (like corequisite developmental courses) or to improve degree completion in programs that are underperforming on performance metrics. (1.5)
Environmental Responsiveness: COVID-19 and the move to online will likely impact the success of strategies such as corequisite courses and so assessment will need to consider the impact of the pivot to online in Spring 2020 and more online courses in Fall 2020. Any comparisons to prior or future years will need to take into consideration the vagaries related to the pandemic. (1.75)
Summary:
There were individual strategies and units with multiple ongoing strategies assessed. Consideration of the success of these strategies was difficult due to the range of assessment within and between units and the lack of assessment planning by many of the units. This indicates a need for more centralized support of assessment for Intentional Focus #1.
The 5 units that submitted reports has average effectiveness scores ranging from 5.375-7.75 for an average effectiveness score of 6.75. None fell into the ineffective range. The majority of these programs could improve effectiveness by more formally developing and implementing assessment plans in a way that allows them to use assessment to inform decision-making.
Table 1.2: Institutional Effectiveness Scale
|
Performance |
Ineffective |
Effective |
Exceptionally Effective |
|
Average Effectiveness Score* |
0-4 |
5-8 |
9-10 |
|
|
On average strategies are not effective and not resulting in changes that improve effectiveness
|
On average strategies are meeting performance thresholds, are helping the institution improve performance on IF indicators, and are using assessment to inform changes to their programs. |
On average strategies are exceeding performance thresholds, using assessment to improve performance and responding as needed to the changes in the environment |
|
*Lower average scores for an IF will be explained by the IFSET who may recommend abandoning ineffective strategies and adopting new strategies |
|||
Recommendations from IFSET to help improve strategies, assessment, and contribute to aligning strategies with institutional objectives:
These units are doing very good work and many are undertaking new strategies to support goals in IF #1 with little new investment. We do suggest that MSU focus future assessment of IF #1 for accreditation purposes on cornerstone programs where the institution has/is investing substantial resources and on promising pilot programs where the institution might consider investing more if the program(s) are effective.
The team also recommends working with units on campus that will do assessment of strategies for IFSET #1 to develop a more appropriate assessment process and to make sure the units are using and documenting how they use the assessment data to inform future programming.
We might also want to work with the budget office and the units to come up with some way to measure the resources invested in some of these strategies.
Appendix 1: